Understanding Relational and Non-Relational Databases
If you’re planning to build a complex network you need to first start small one step at a time. To start small something simple we will talk about single server setup in this post.
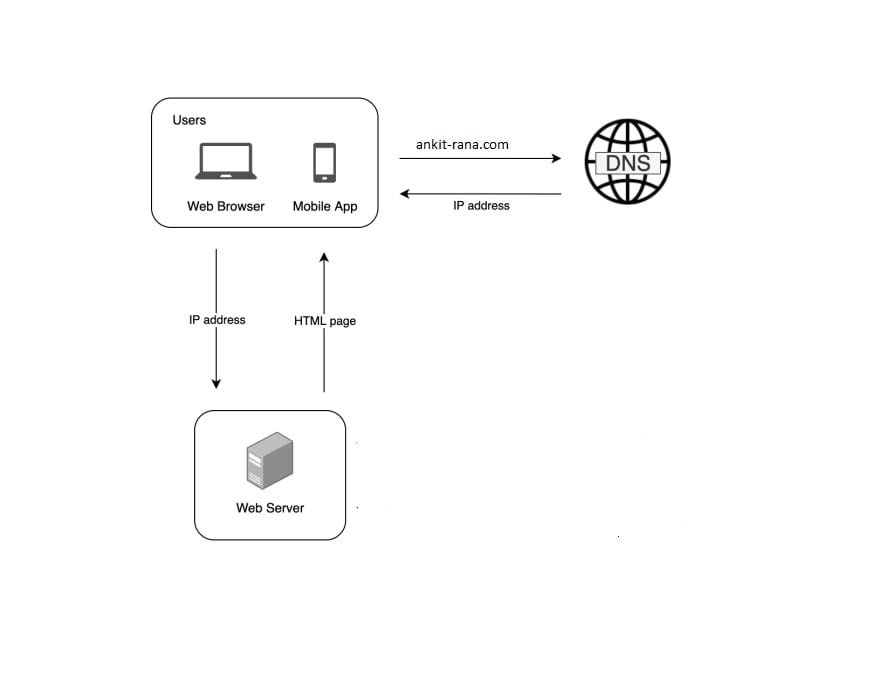
Request flow from User to the web server:
-
- User is going to access website through domain name such as ankit-rana.com.
-
- Internet Protocol (IP) is returned to the web browser or app via DNS (Domain Name System) Look-up for example: 12.123.23.200
-
- Once IP is obtained, web server receives HTTP (Hyper Text Transfer Protocol) request directly.
-
- Usually web-server returns HTML pages or JSON as response.
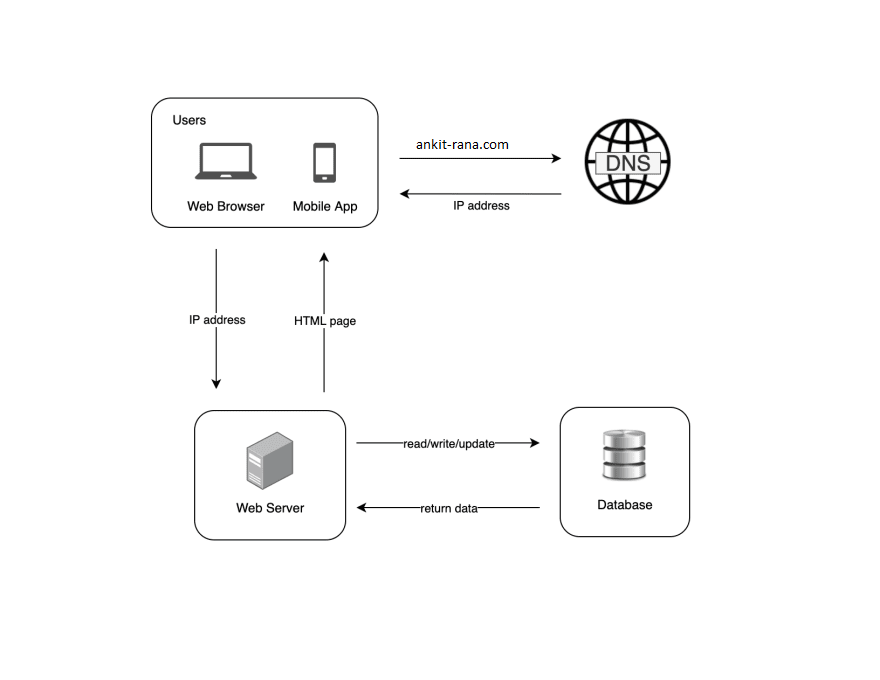
As the scale of your service or application increases i.e. more and more new users onboard one server will no longer be enough and there will be a requirement for multiple servers. Also, to save the information of your users you need to a database. Database will act as your persistent storage.
With increase in number of requests its important to scale your server and separating web tier and data tier is an important step to scale the servers and databases independently.
Which database to choose?
| Relational Database | Non-Relational Database | |
| 1 | Relational databases represent and store data in tables and rows. You can perform join operations using SQL across different database tables. | Non-Relational Databases are grouped into four categories: key-value stores, graph stores, column stores, and document stores. Join operations are generally not supported in non-relational databases. |
| 2 | Relational databases are also called a relational database management system (RDBMS) or SQL database. | Non-Relational databases are also called NoSQL databases. |
| 3 | Example: MySQL, Oracle database, PostgreSQL, etc. | Example: CosmosDB, Cassandra, HBase, Amazon DynamoDB, etc. |
When to use Non-Relational databases?
-
- Application requires super-low latency.
-
- Data is unstructured, or there isn’t any relational data.
-
- There’s only need to serialize and deserialize data (JSON, XML, YAML, etc.).
-
- There’s massive amount of data to store.
Understanding Horizontal and Vertical Scaling
You can scale your applications in two ways:
- Vertical Scaling
- Horizontal Scaling
| Vertical Scaling | Horizontal Scaling | |
| 1. | Vertical scaling is referred as “scale up”, which means the process of adding more resources (CPU/Memory) to your servers. | Horizontal scaling is referred as “scale-out”, which means it allows you to scale by adding more servers into your pool of resources. |
| 2. | Only suitable for applications with low traffic and is simpler. | It is more desirable for large scale applications. |
| 3. | Hard limitation on the number of resources that can be configured to a single server. | No limitation on resources as multiple servers can be added. |
| 4. | No failover and redundancy, application will go down incase server goes down. | Multiple instance of the same application is running at a time so incase on of the instance goes down other one will take its place and distribute the load. |
Load Balancer
Load balancer is used to distribute incoming traffic among web servers, that are defined in a load-balanced set.
Your service can run in multiple regions, example South Central US, East US, etc. Each instance running in these regions/clusters will will have a unique cname and you directly interact with that instance using this cname. But your client user can’t manage all these cnames to interact with your service. Load-Balancer will manage the traffic to all these cnames internally depending upon the configuration set at GSLB (Global Server Load Balancer) .
The service will have an ingressHost i.e. GSLB endpoint which user/client will interact and internally from this ingressHost cnames will get the request from load balancer.
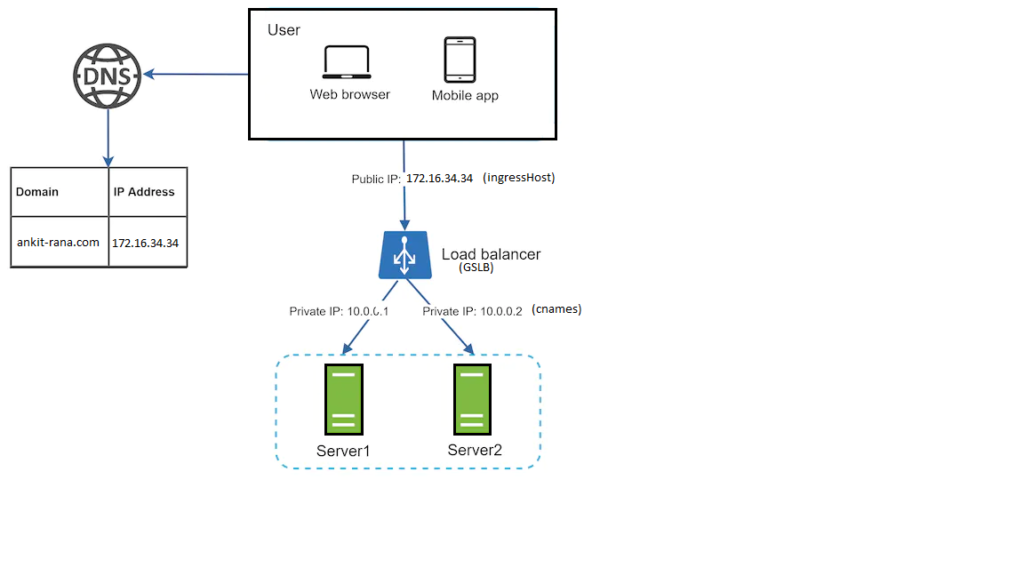
User connect to the public IP (ingressHost) of the load balancer. Due to load balancer in place, clients can’t reach web servers directly. To enhance the security, private IPs (cnames) are used for communication between servers. Private IP is an IP address that is reachable only between servers with in the same network (intranet). It is unreachable over the internet. The load balancer acts as an intermediate layer that communicates with web servers through private IPs.
Load balancer will take care of failover issues and will be redirecting traffic to the healthy instances of the service. Thus, it has helped in improving the availability of web tier.
How does load balancer act in failover situations?
- If server 1 goes down, all the traffic will be routed to server 2. This prevents the website from going offline. We will also add a new healthy web server to the server pool to balance the load, once the new server is up load will be distributed again by load balancer.
- Incase resources are less to handle the traffic load of the website, the load balancer will again come into the picture to scale the infra. All that is needs is to add more servers to the web server pool, and then once the set threshold for resources is met load balancer automatically increase the server and starts to send requests to them.
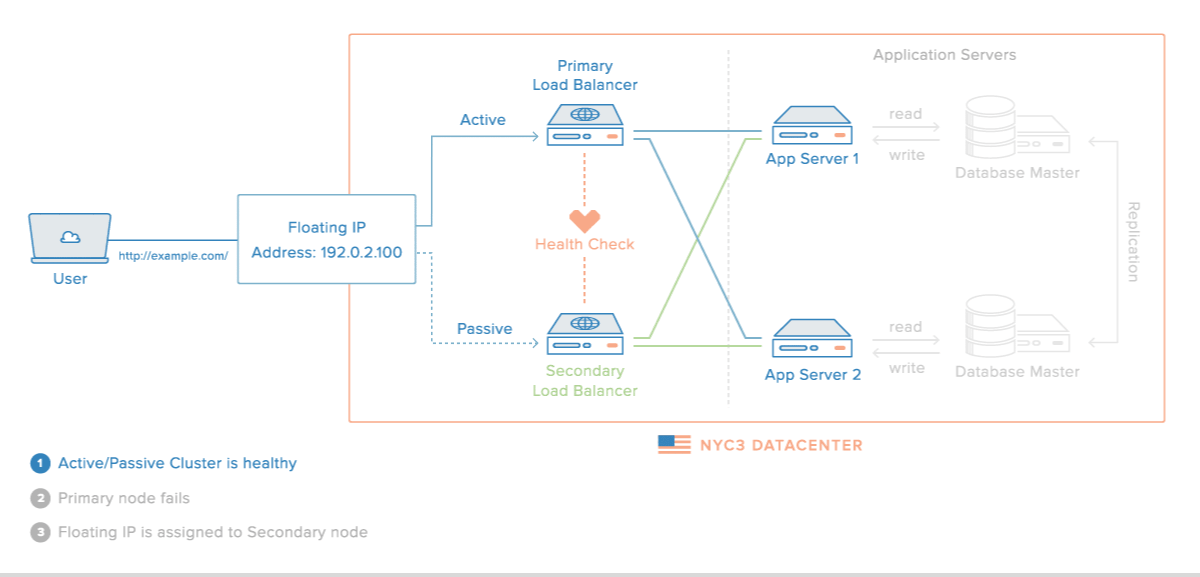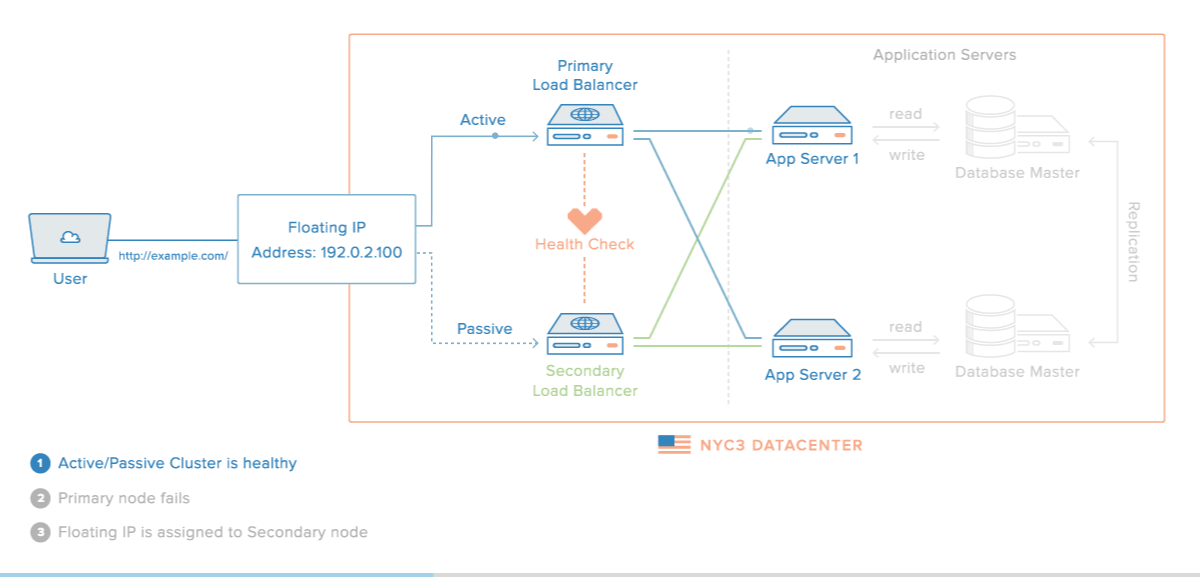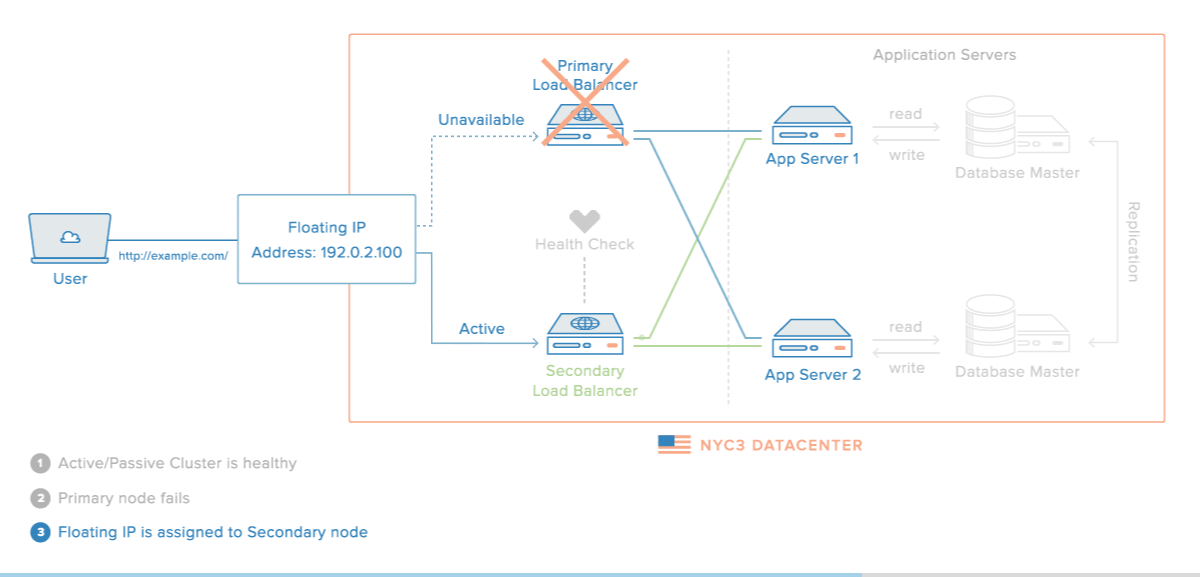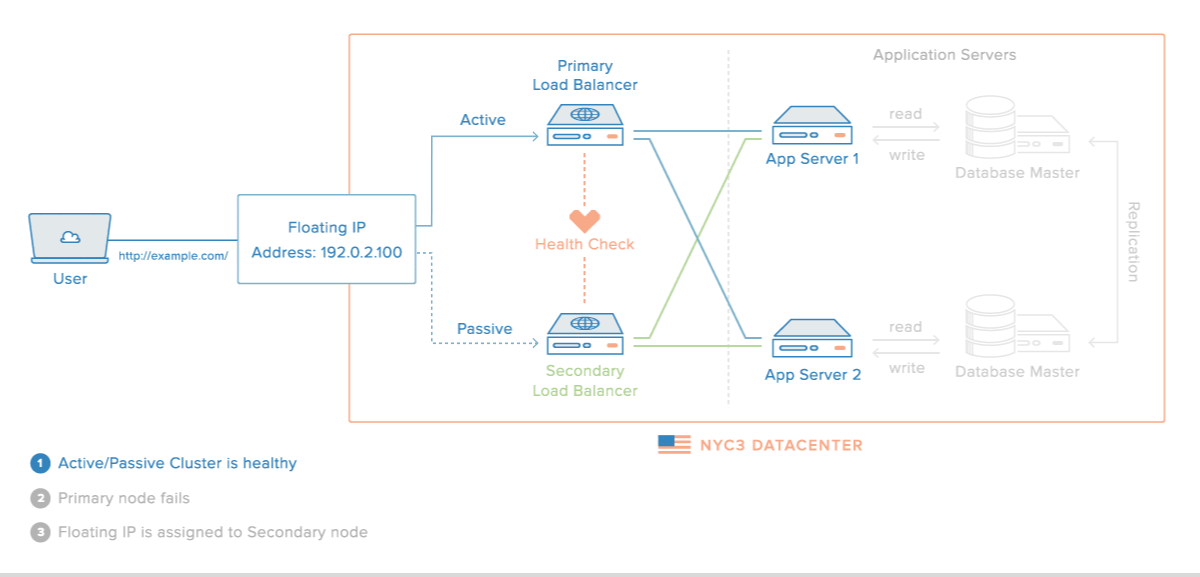
Understanding DB Replication and Handling Failovers
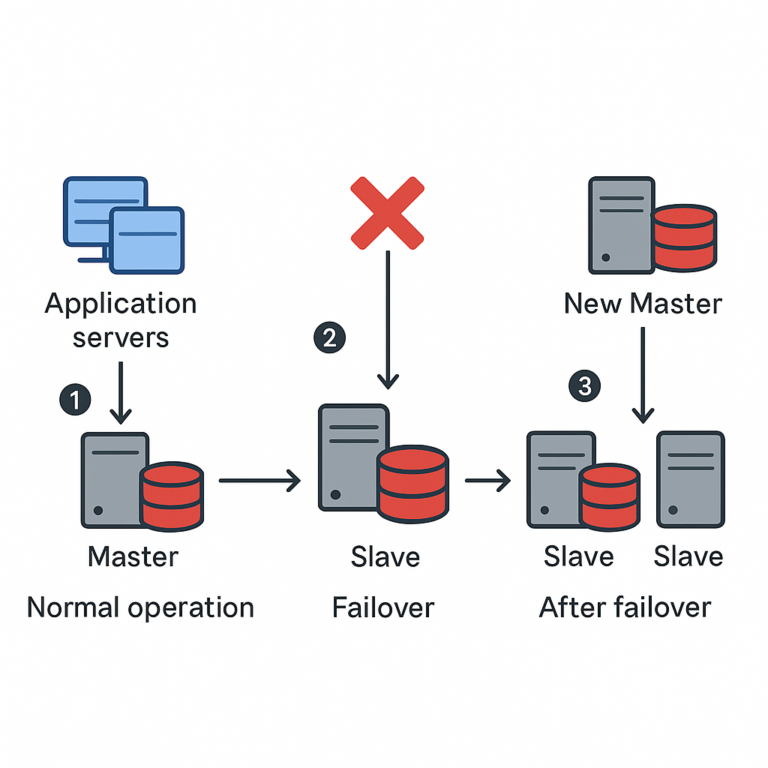
In order to handle server failover, we learnt about Load Balancer and how shifts traffic from one server to another. The same situation can happen for database also what if your database goes down? How are you going to handle this situation?
Similar to multiple servers inside Database also we have multiple instances or database replicas. Each of these replicas are kept in sync by the process of Database Replication. “Database Replication process can be used in many Database Management Systems, usually it is with a master/slave relationship between the original (master) and the copies (slaves)”.
Usually all the write operations are supported only by master database and slave database serves read operations. Slave database gets the copies of data from master database by database replication. Write operations include the commands which modify the data example: insert, delete, update, etc. The number of read operations that happens inside a database is usually greater than the write operations thus number of slave databases in a system is larger than number of master databases.
What are benefits of database replication?
Master-Slave architecture increases the overall performance of the database as write operations happen only at master database and reads happen at slave databases. This separation of roles improves the performance by increasing parallelism.
Incase of DR / disaster is one of the database server goes down then still data will be saved/preserved as it is present at multiple locations. Database replication will ensure no data is lost from any database server.
High availability of your website is ensured by database replication as even if one of the database server goes down still other database servers will serve the requests.
What if the master database goes down?
If master database goes down/offline then a slave database will become master database, all the write operations will be executed temporarily on the newly created master database. Along with it a new slave database will be created which will replace the previous one for data replication. In real world scenarios promoting a slave database to master database is a complex process as slave database may or may not be upto date or sync with master database. The data which is missing or absent needs to be recovered manually via some scripts. Other ways to solve this problem would be to have multi-master database model or better data replication process such as circular replication, not to mention these methods will increase the complexity of your setup.
What if slave database goes down?
If there’s only one slave database and that goes down then master database will serve both read and write traffic. Also, another slave database will be created after finding the issue and traffic will again be re-routed to slave database. Incase there are multiple slave databases then read-operations will be routed to another slave database which is still healthy and here also, another slave database will be created after finding out the issue.
Multi-Master Database Setup
Master Slave Database Setup
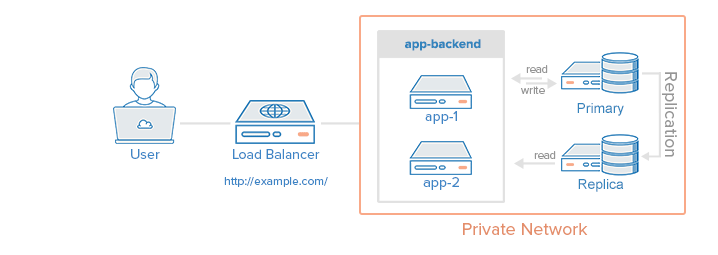
Understanding Caching
Loading data from the database every time user makes a similar request can increase the API response time. In such cases Cache can be used.
What is a Cache?
Cache is a temporary data storage layer which is much faster than database. Cache works like map, which has a key and value every time you enquire for that key it’s corresponding value is returned. The benefits of having separate Cache will create better performance and would also reduce the DB hits or Database calls.
User makes a request to the application, now application is going to check for the given request/key data is present inside Cache or not, if Cache contains the data then read from the Cache. If Cache doesn’t contain data then read from Database and save this data into the Cache. This process is called read-through cache.
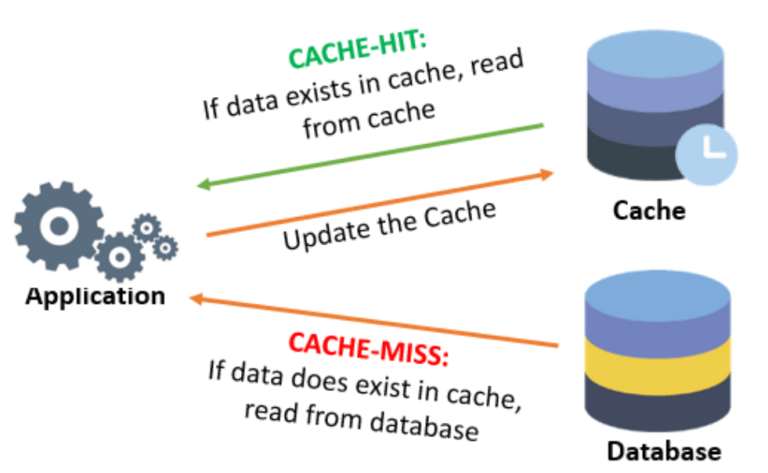
When to use a Cache?
Cache should be used when the data is read frequently but modified infrequently. Data inside Cache is stored inside volatile memory and thus it is not created for persisting data. If Cache server restarts then the data present inside memory will be lost. Therefore, you can not just rely on Cache for storing all your data and you should always store data inside persistent data stores.
Every cache that you configure should have an expiration policy. Once cached data expires it will be removed from the cache. If expiration policy is not in place then data inside Cache will be stored permanently unless Cache memory becomes full. Your expiration date should should not be too short as this will cause Cache misses and database calls will increase significantly. At the same time it should not be too long as the cached data can become stale.
It is important to keep your database and cache in sync. Inconsistency can happen because of database being modified and not updating cache in the same transaction.
You should have cache servers across different data centers as if a single cache server exists then there can be “A Single Point of Failure” (SPOF) and it will stop entire system from working. One more thing that can be done to present failure would be to configure memory more than that is required.
What will happen if the Cache memory becomes full?
Once Cache memory is full, any new items which are added to it will cause removal of existing items. This process is known as Cache Eviction. Least-recently-used (LRU) is one of the most popular Cache eviction policy.
Understanding CDN
Content Delivery Network
Content delivery network is a network of servers which are geographically dispersed and are used to deliver static content to the user. Some examples of static content include: Images, videos, CSS, etc.
How does CDN works?
Whenever a user visits website then CDN server which is closest to the user is going to deliver above mentioned static content. This has two advantages: First, user requests are served faster and second website loads are faster. But with increase in the distance of user from the server will increase this website load time.
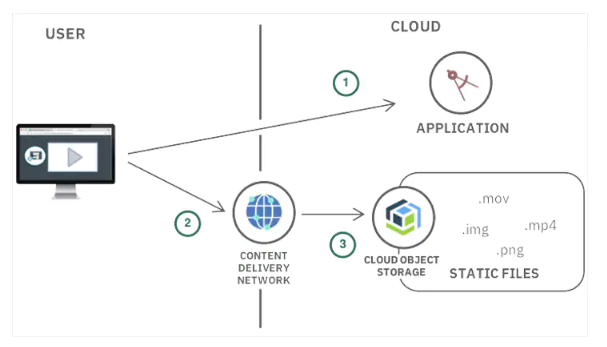
Whenever user tried to static content from the website using it’s URL. CDN server will try to fulfil this request by checking for this content in it’s storage. If CDN server doesn’t have it, then it will request the file from the origin or online storage. The origin is going to provide the requested content and will provide an optional HTTP header TTL (Time to live) which will describe for how long your content is cached. CDN server caches the content/file and returns it to user. File will stay in CDN server until TTL expires. Now if there’s any user who requests for the same file then CDN sever will return the file from its cache if it’s TTL has not expired.
Things to Consider before using CDN:
CDNs are usually run by third party service providers and you will be charged for the data transfer that happens in and out of CDN. So cost is one of the factors you should consider before using CDN.
Incase CDN server goes down your application should have backup plan and it should detect the issue and do the needful like if CDN server is down serve requests directly from origin till CDN server is restored.
TTL for your static objects should be set as per the content which has to be stored. There can be time sensitive content and having a short TTL for such content is really important. Similarly, TTL should not be vert small or big. As this will simply either increase the loading of content from the server instead of CDN Cache or will serve stale content to the user.
Understanding Stateful and Stateless Systems
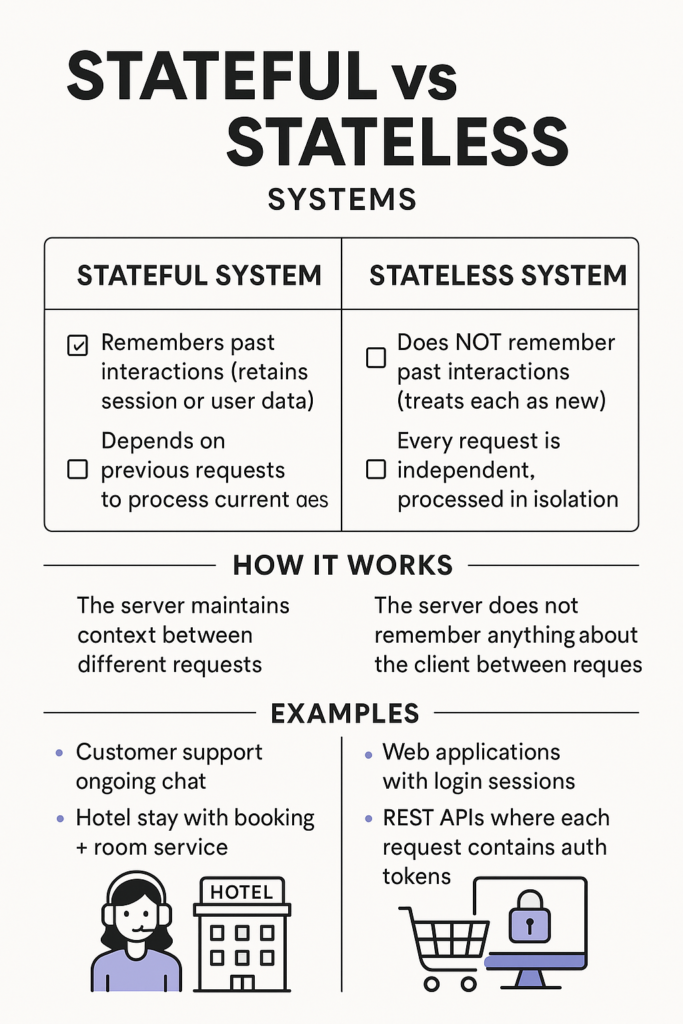
A stateful system is one that remembers past interactions or data, which allows it to provide more context-sensitive responses over time. In contrast, a stateless system does not retain any history of previous interactions; each request is processed in isolation as if it were the first time.
Stateful Systems
-
Memory of Past Interactions:
-
A stateful system keeps track of previous interactions or sessions. This means that information from earlier communications or transactions can be referenced and used in later interactions.
-
Example: In an online shopping website, a user’s shopping cart is an example of a stateful component. The website remembers the items you added to your cart during your session, even as you navigate different pages.
-
-
Context Awareness:
-
Because the system retains state, it can provide responses that are tailored to the user’s previous actions or preferences.
-
Example: Consider a video streaming service that recommends shows based on your viewing history. The system “remembers” what you’ve watched and uses that information to suggest similar content.
-
-
Complexity in Management:
-
Maintaining state requires additional mechanisms like session management, cookies, or databases to store state information. This can add complexity to system design and scalability challenges.
-
Example: Multiplayer online games use stateful systems to track player progress, scores, and game states in real time. This is essential for the game to function properly but requires robust systems to manage state across many users simultaneously.
-
Stateless Systems
-
No Memory of Past Interactions:
-
A stateless system treats each interaction as a new, independent event. There is no memory of previous requests, so each request must contain all the information needed to complete it.
-
Example: The HTTP protocol is inherently stateless. When you click a link or submit a form, the server processes that request without any reference to previous requests unless additional mechanisms (like cookies or tokens) are implemented.
-
-
Simpler Design:
-
Since there is no need to store session information, stateless systems are generally easier to scale. Each request is handled independently, which simplifies load balancing and resource management.
-
Example: RESTful web services are designed to be stateless. Each API call includes all necessary parameters (like authentication tokens and data payloads) for the server to process the request, making the system more robust and easier to distribute across multiple servers.
-
-
Reliability and Fault Tolerance:
-
Stateless systems are often more reliable because there is no dependency on previous states, reducing the chance of errors due to lost or corrupted session data.
-
Example: A serverless function (like those provided by AWS Lambda) is stateless by nature. Each function invocation is independent, ensuring that if one request fails or the system scales up to handle more requests, previous interactions do not affect the new ones.
-
Scalability
If you want to scale your web server horizontally then you should move the state out of web server. If your application stores some state in it then you need to make sure all the request belonging to that state are served by that particular server. For this you would need to implement service to service routing technique based on some condition. For example: If you are getting requests belonging to a particular product then only server ‘1’ should serve those requests as information related to state product is only present on that server. Due to these reasons it is a good practice to store session data in persistent storage such as NoSQL database.
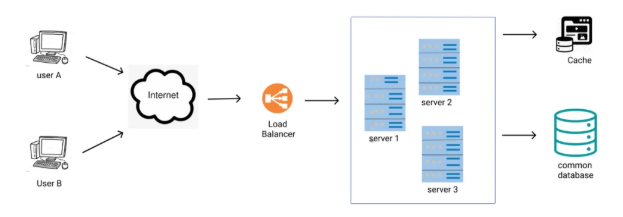
In stateless architecture the above mentioned problem doesn’t exist as HTTP requests from users can be sent to any web servers, which will fetch the state data from common/shared database/storage. State data will be stored in a shared data store and will be kept out of web servers. Thus, a stateless architecture system is more robust, simpler to understand and implement and most importantly scalable.
If your user requests increase and servers need more resources you can easily enable auto-scale and solve this issue as there’s no dependence of state on any of the server.
Understanding Async Communication and Monitoring
Multi-Data Center Setup:
User requests are geo-routed depending upon the closest data center to their geo location. For example there are 2 data centers US-Scus and US-WEST then requests will be distributed as x% in US-SCUS and remaining (100-x%) in US-West. This process of geo-routing is done by geoDNS service which allows domain names to be resolved to IP addresses based upon geo location of the user.
Incase, anyone of the data center goes down then all the requests will be served by other data center.
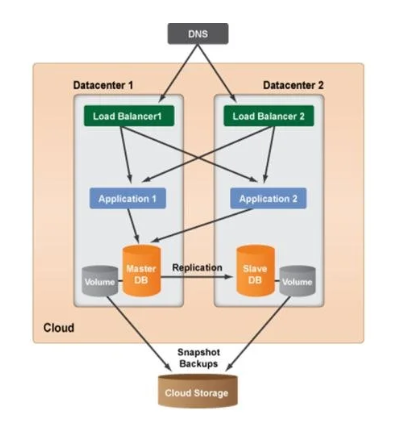
Things to consider in mind to achieve multi-data center setup:
- In order to redirect traffic to the correct data center tools like GeoDNS are required. Which will help in sending traffic from the nearest data center to the user.
- Data must be replicated across multiple data centers so that users from different regions can use different DBs in data centers without any synchronization issues.
- Automated tools should installed for the smooth deployment of applications and applications should be tested in different regions under various conditions like recreating failover situation under controlled conditions.
Async Communication Using Messaging Queue
Message queue is stored in memory and used for supporting async communication. It will act as a buffer for async requests. There are two components in a messaging queue architecture producer and a consumer.
Services which insert messages are called producers/publishers they create messages and insert it into a message queue. Services which listen to these messages are called listeners/consumers/subscribers.
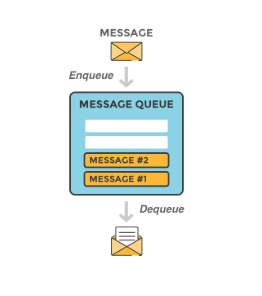
One of ways to understand publisher/subscriber model in messaging queues is to work with Kafka. Decoupling message queue makes a system more scalable and reliable. Now, publisher has no dependency on consumer to send message at a particular time. Publisher can publish the message any time and whenever consumer is available then it can consume that message. Messages will stay in the queue for given retention time set by the admin. Also, both producers and consumers can be scaled independently.
Monitoring & Alerting
As you grow your business and number of users increase significantly then it is important to invest in alerting and monitoring tools.
Proper logging, alerting and monitoring is important as it helps to identify errors and problems in the system. With increase in the number of services it becomes difficult to be at the top of each component in the system and what is the current status of the system but if you have tools which not just tells you about the system health but also the data related to users which you can further analyze to understand user behavior and take right decisions for them. Some of the commonly used tools include: Grafana, Prometheus, Splunk, ELK, etc.